Triatoma rubida and Triatoma protracta
What is a Kissing Bug?

Also known as an assassin bug, the kissing bug belongs to the Reduviidae family of ambush predators. This insect, like the bed bug, is a hematophage in which it sustains itself by drinking the blood of a host. Some species of kissing bug develop wings to reach their host, however wings are exclusive to only the adult stage and not all species develop wings as an adult. This insect feeds on a host by using its long needle like beak, called a proboscis, to take a blood meal. This insect typically feeds on sleeping animals and humans. Known to bite around the eyes and mouth, hence the name.
The Assassins Lair

Kissing bugs belonging to Triatoma rubida are located in the Central and North American regions. Those belonging to Triatoma protracta are found in western North American and Mexico. More specifically however they tend to harbor close to the host and come out at night to feed. In barns for instance they like to hide in piles of hay as well as leaf litter and other organic debris piles. They can also use their wings to travel short distance to acquire new hosts.
Do They Carry Disease?

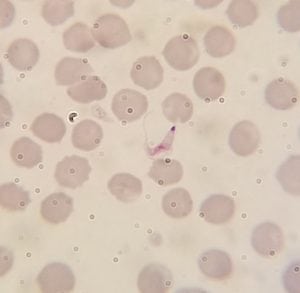
This group of insects is of extreme medical and academic importance in which they are the primary vector of Chagas disease. They spread the disease from host to host, but unlike the mosquito that transmits malaria through saliva, kissing bugs spread Chagas through their feces. Their bite can also cause strong allergic reactions in some individuals.
Chagas Disease Parasite: Trypanosoma cruzi